The Markov analysis module in Reliability Workbench models systems that exhibit strong dependencies between component failures.
Constructing a Markov Model
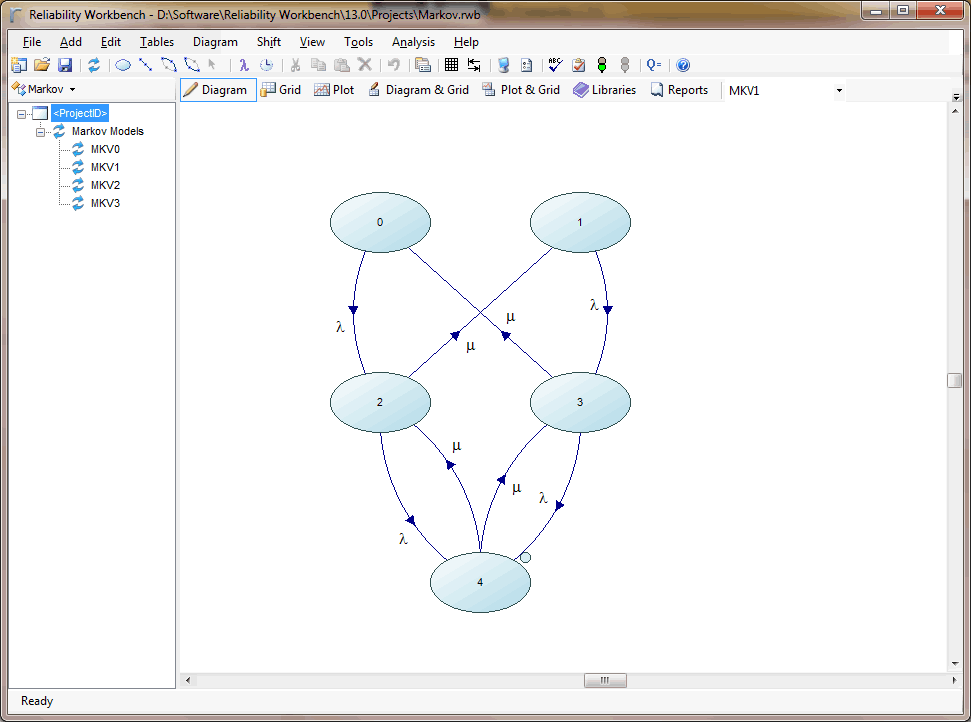
The Markov module provides a visual interface to construct the state transition diagram and then uses numerical integration to solve the problem. The state transition diagram represents the discrete states of the system and the possible transitions between those states.
The Markov module models multiple phases representing continuous or discrete transitions. The module also analyses non-homogeneous processes by allowing time-dependent transition rates to be defined. The phases allow the system lifetime to be split into periods representing (for example) preventative maintenance or standby.
The models created in the Markov analysis module may be linked to basic events in the fault tree and event tree analysis modules.
Markov Analysis Features
- Graphically constructed transition diagram
- Division of analysis into separate phases State attribute editing via easy-to-use dialogs
- Data verification for consistency checks
- Time-dependent transition rates modeled
- Global parameter facility for repetitive data
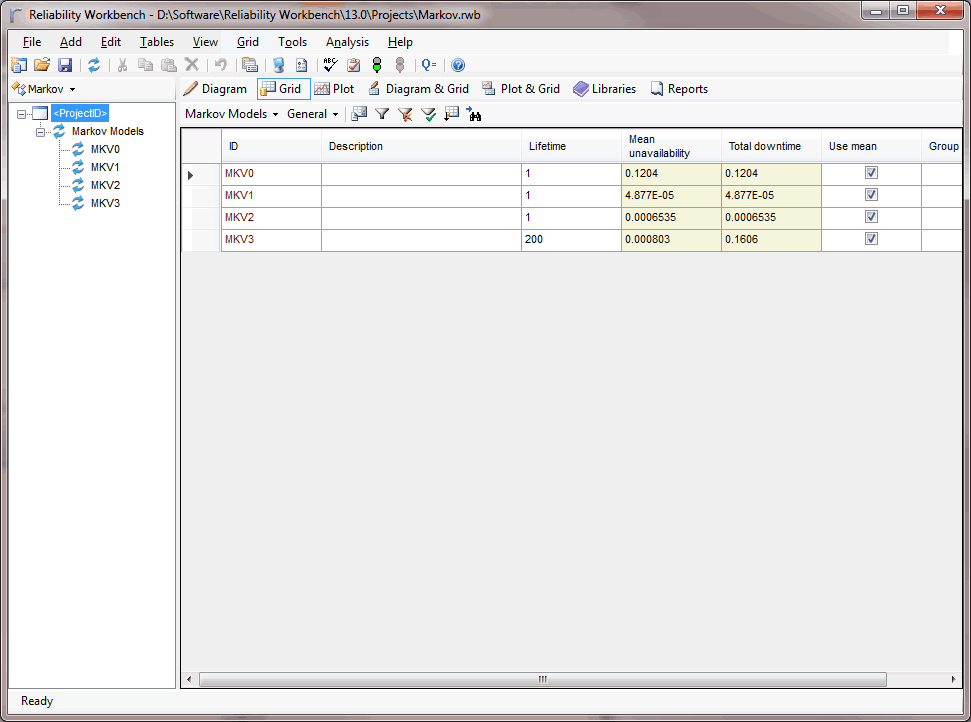
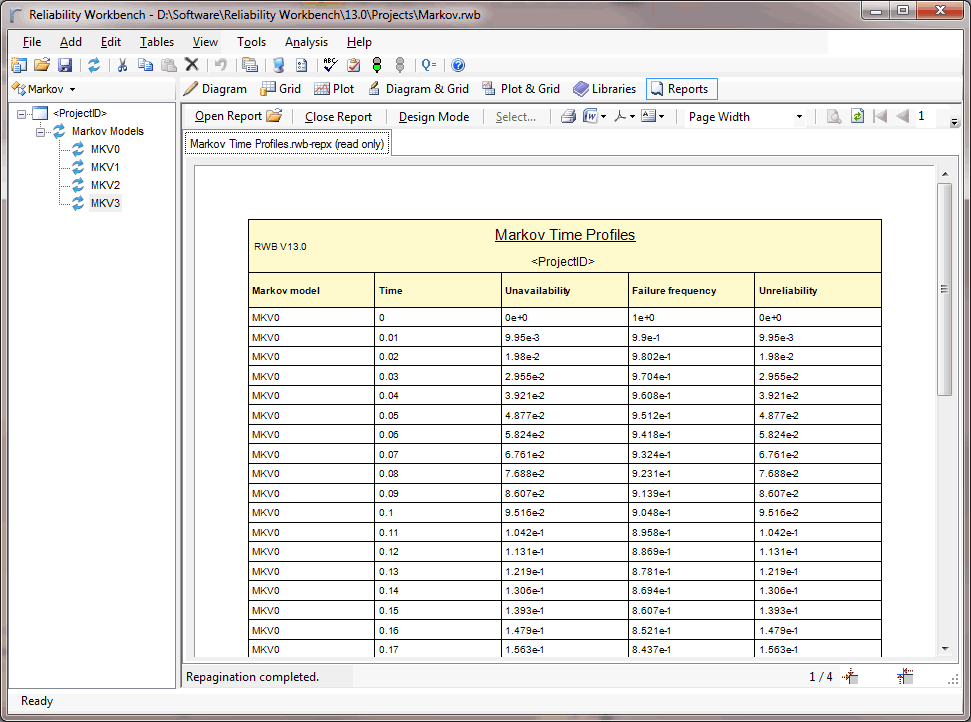
- Calculation of a wide range of probabilities and frequencies
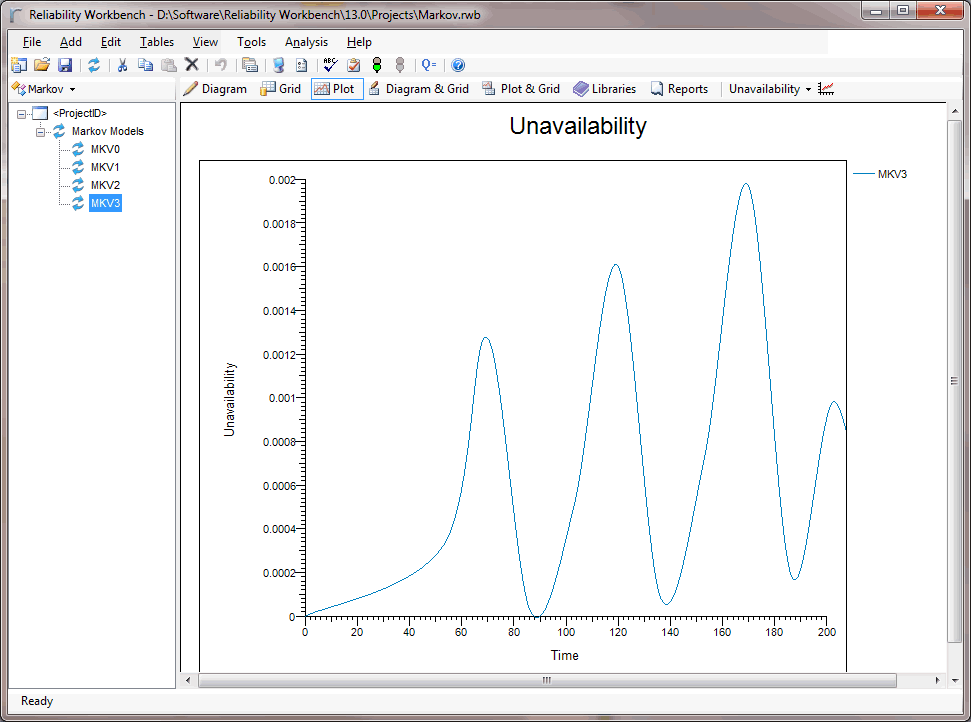
- Graphs and plots showing time-dependent results